Interpreting Deep Learning based Cerebral Palsy Prediction with Channel Attention
Abstract
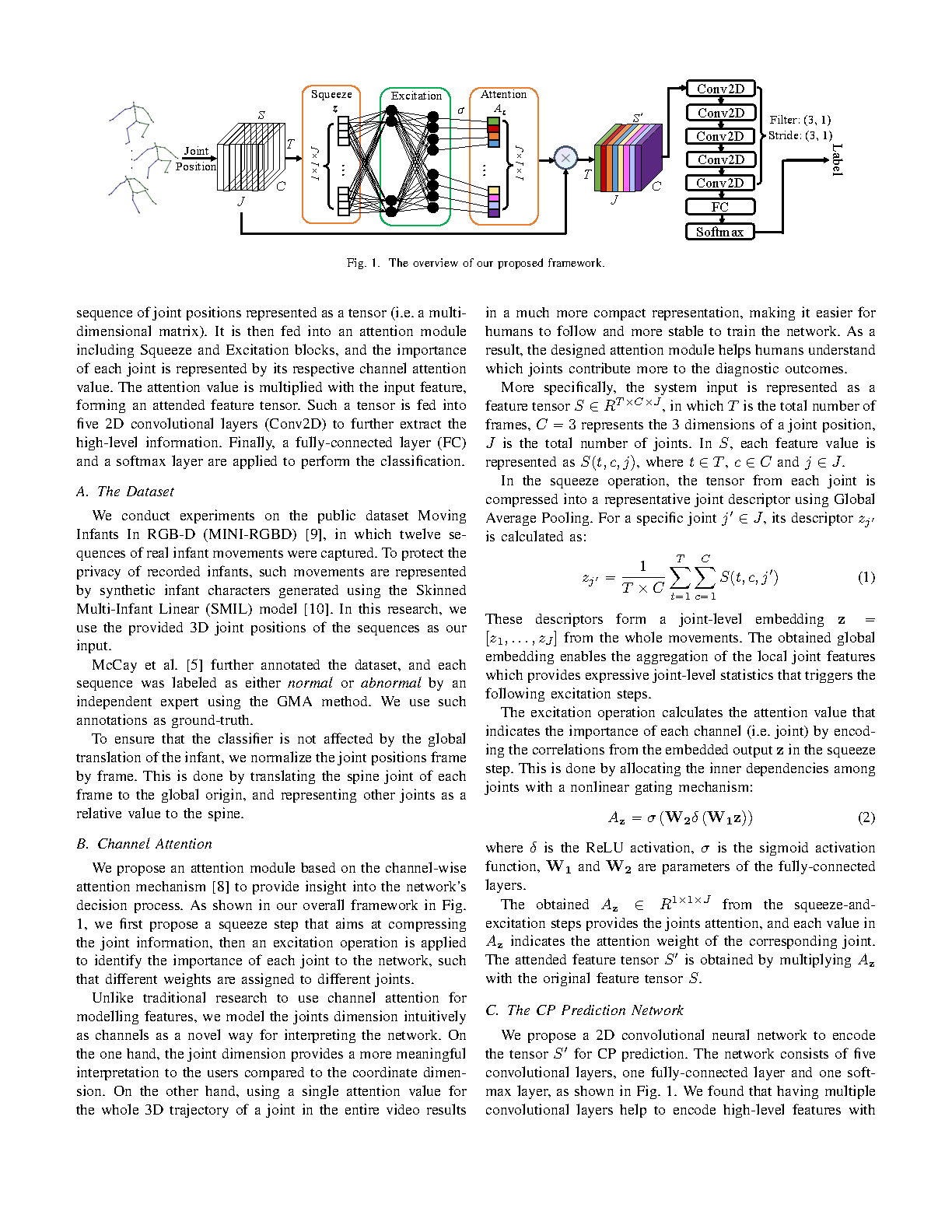
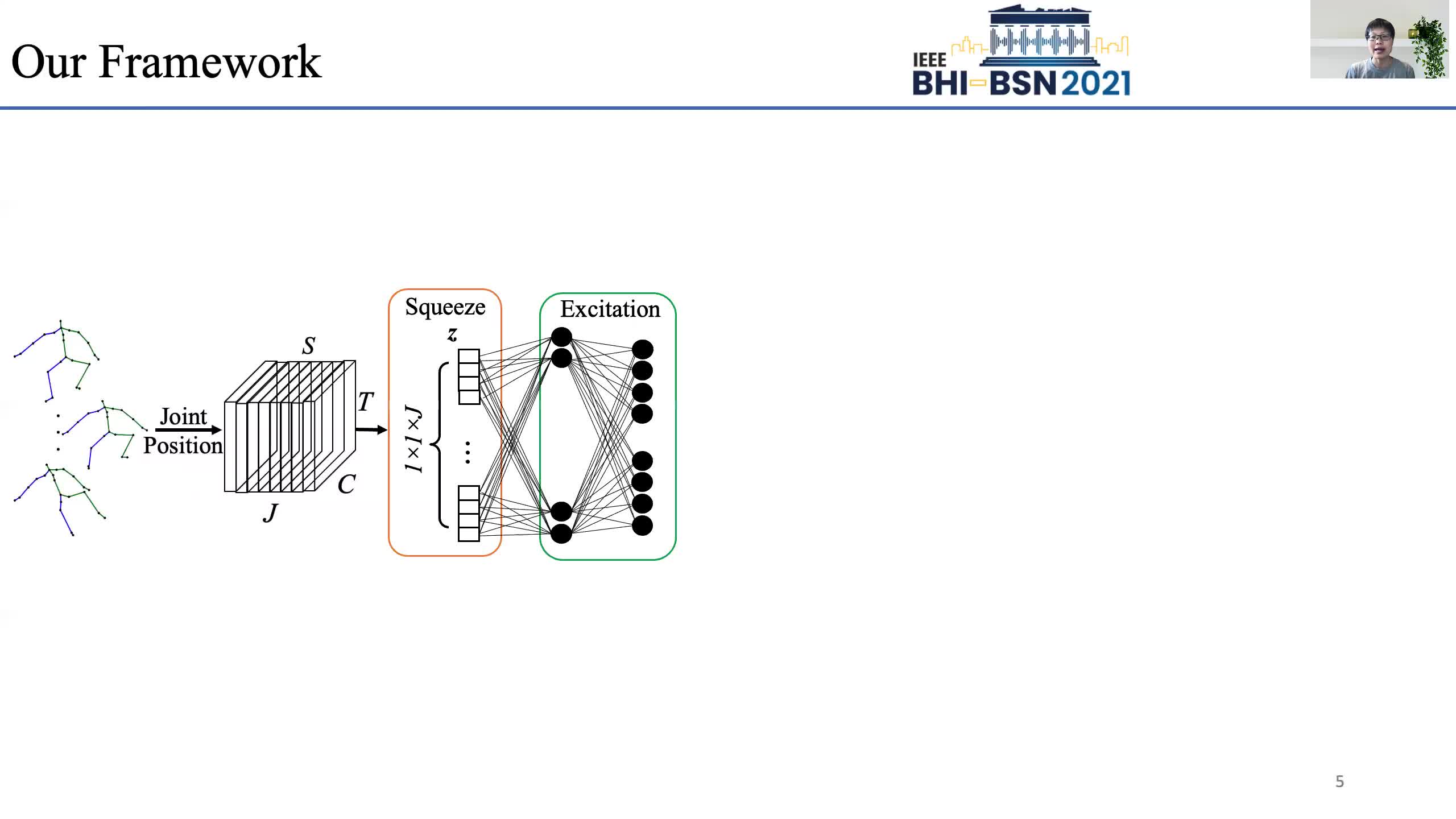
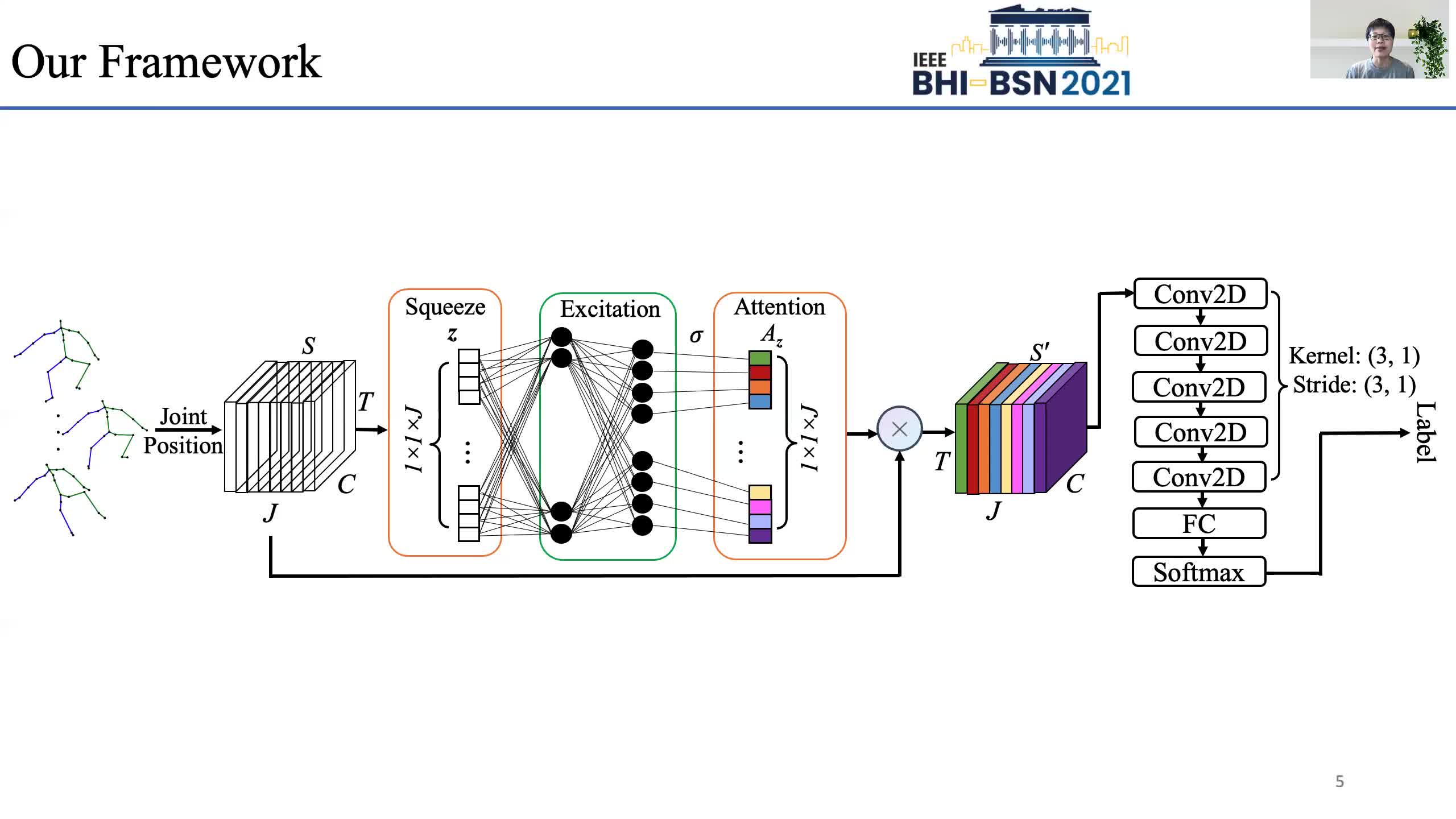
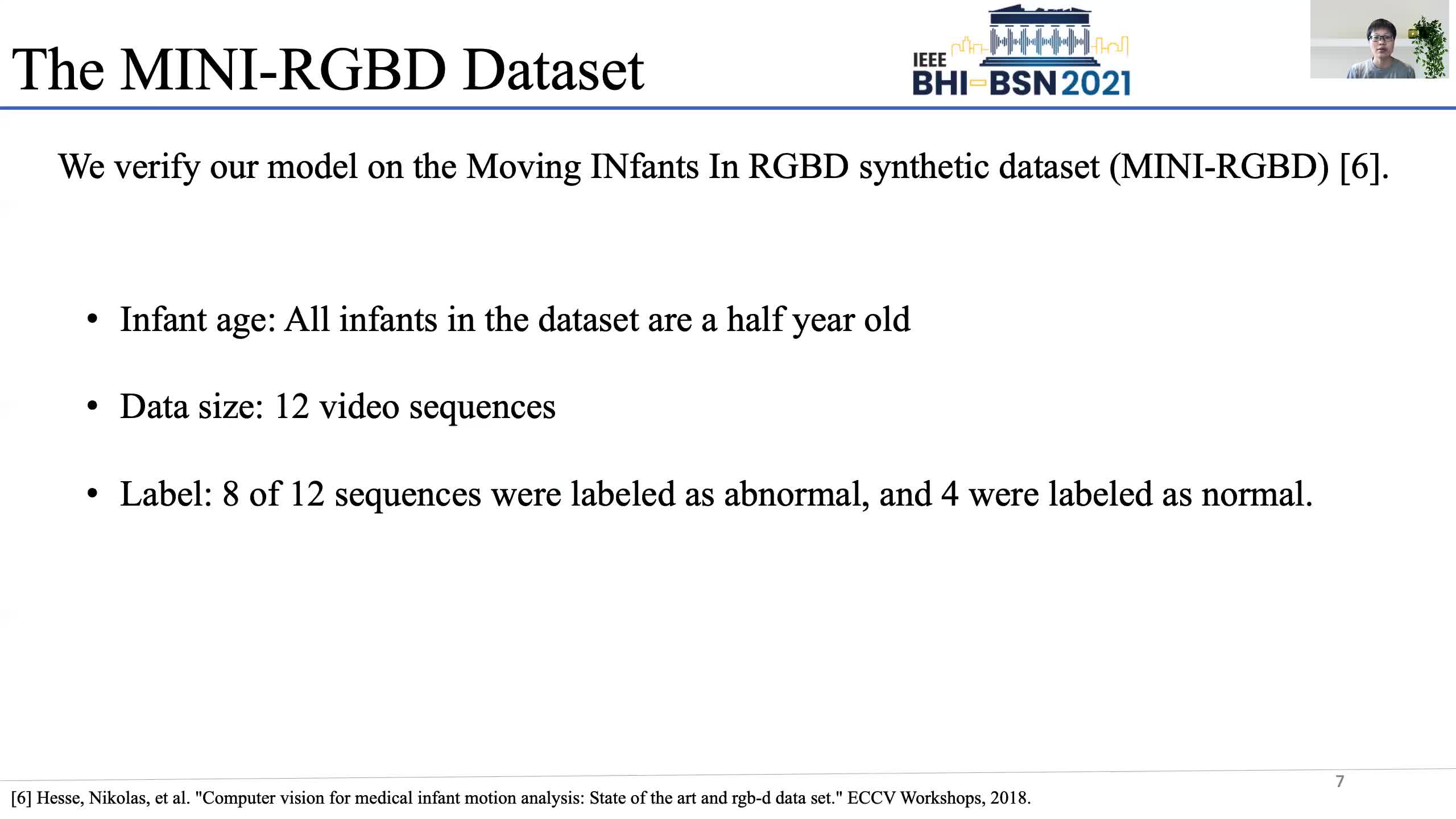
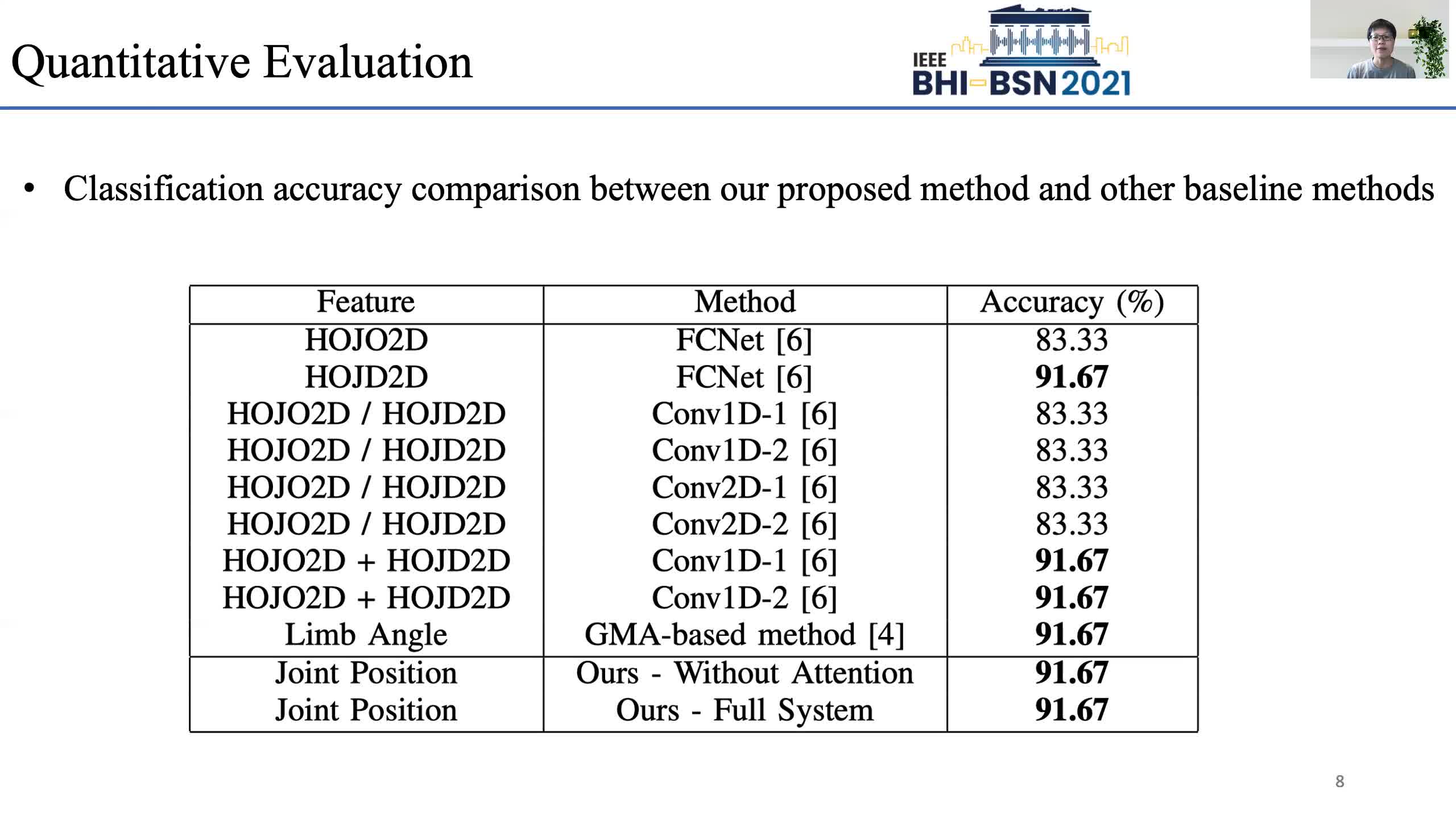
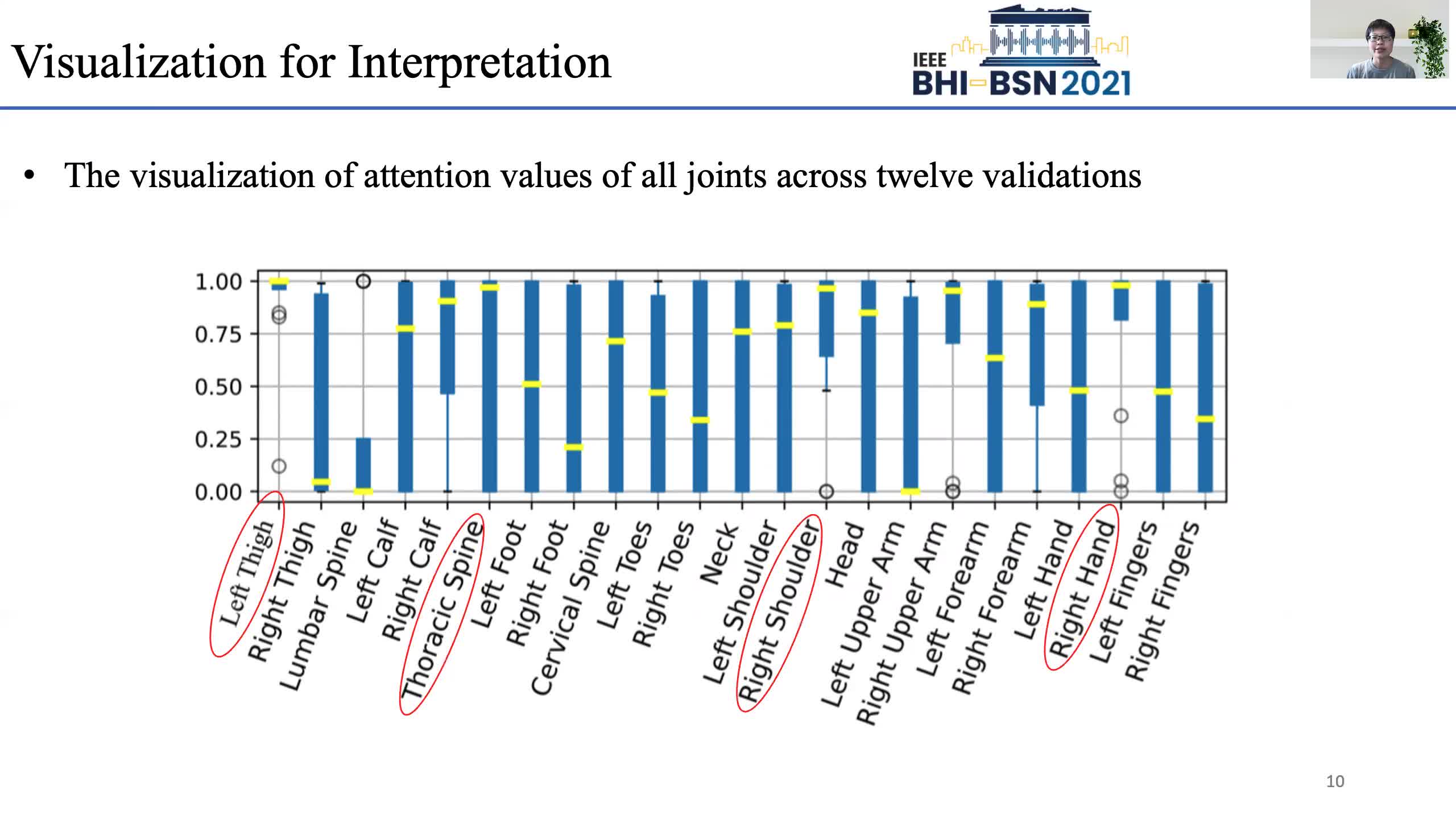
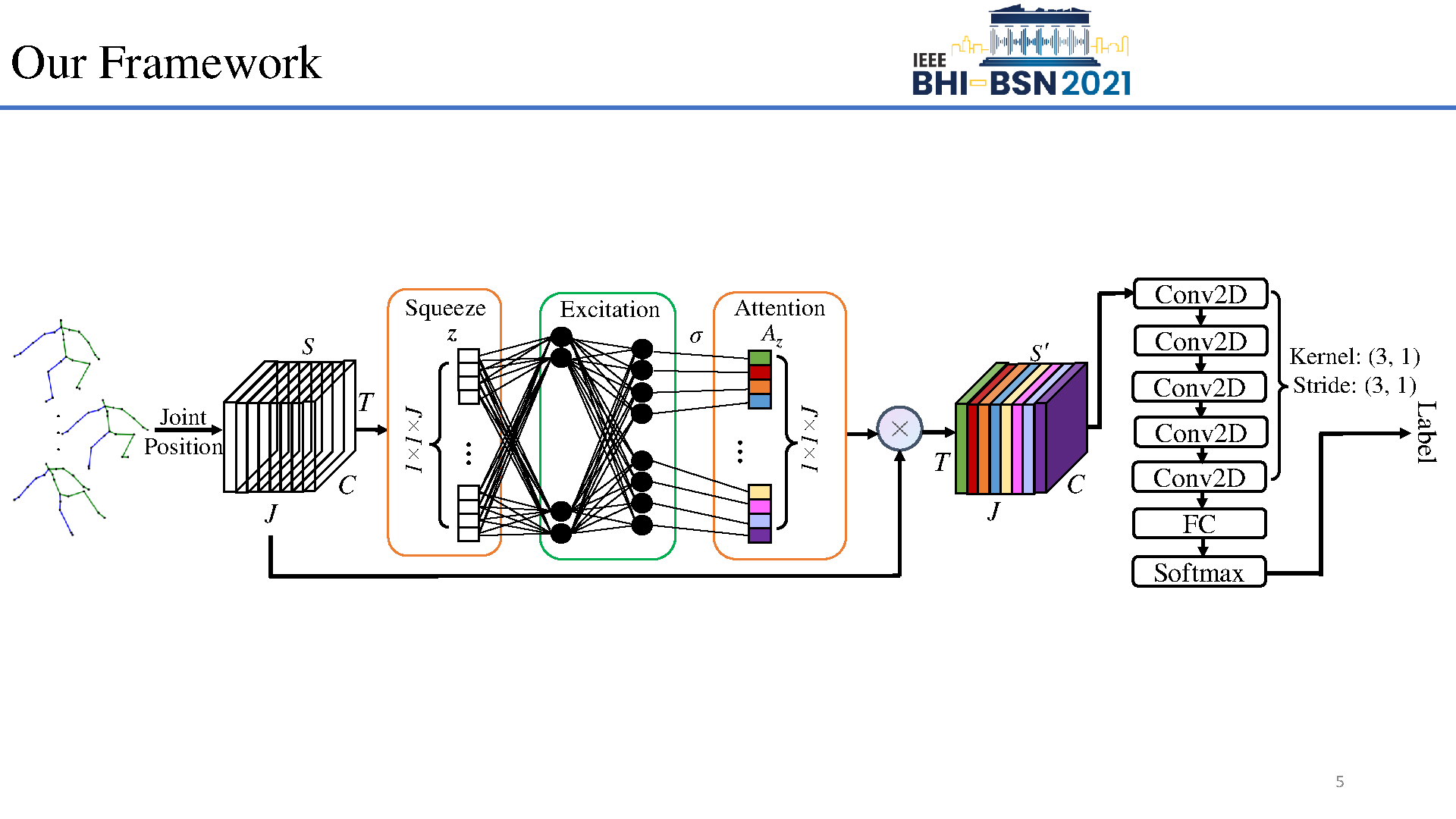
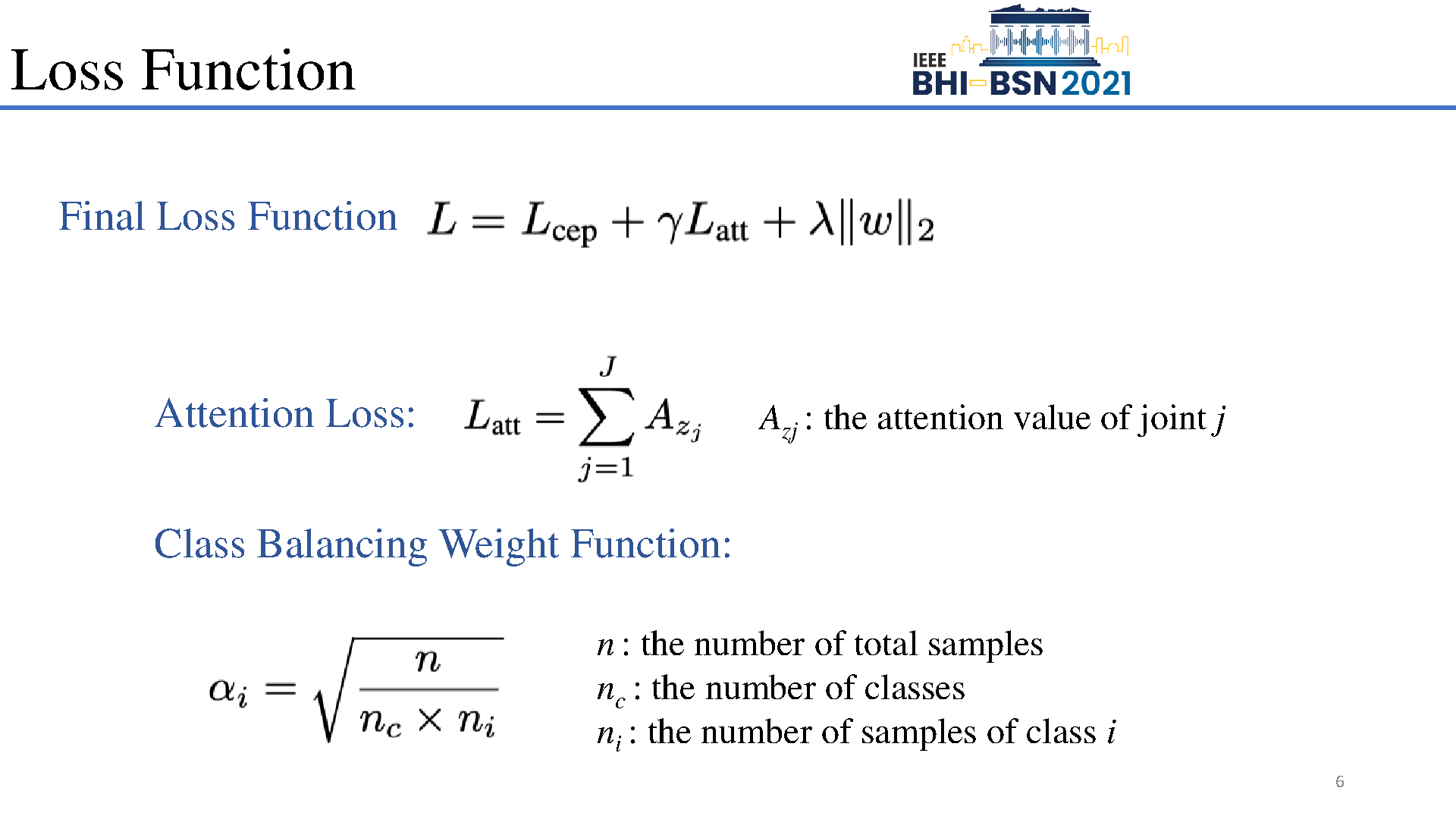
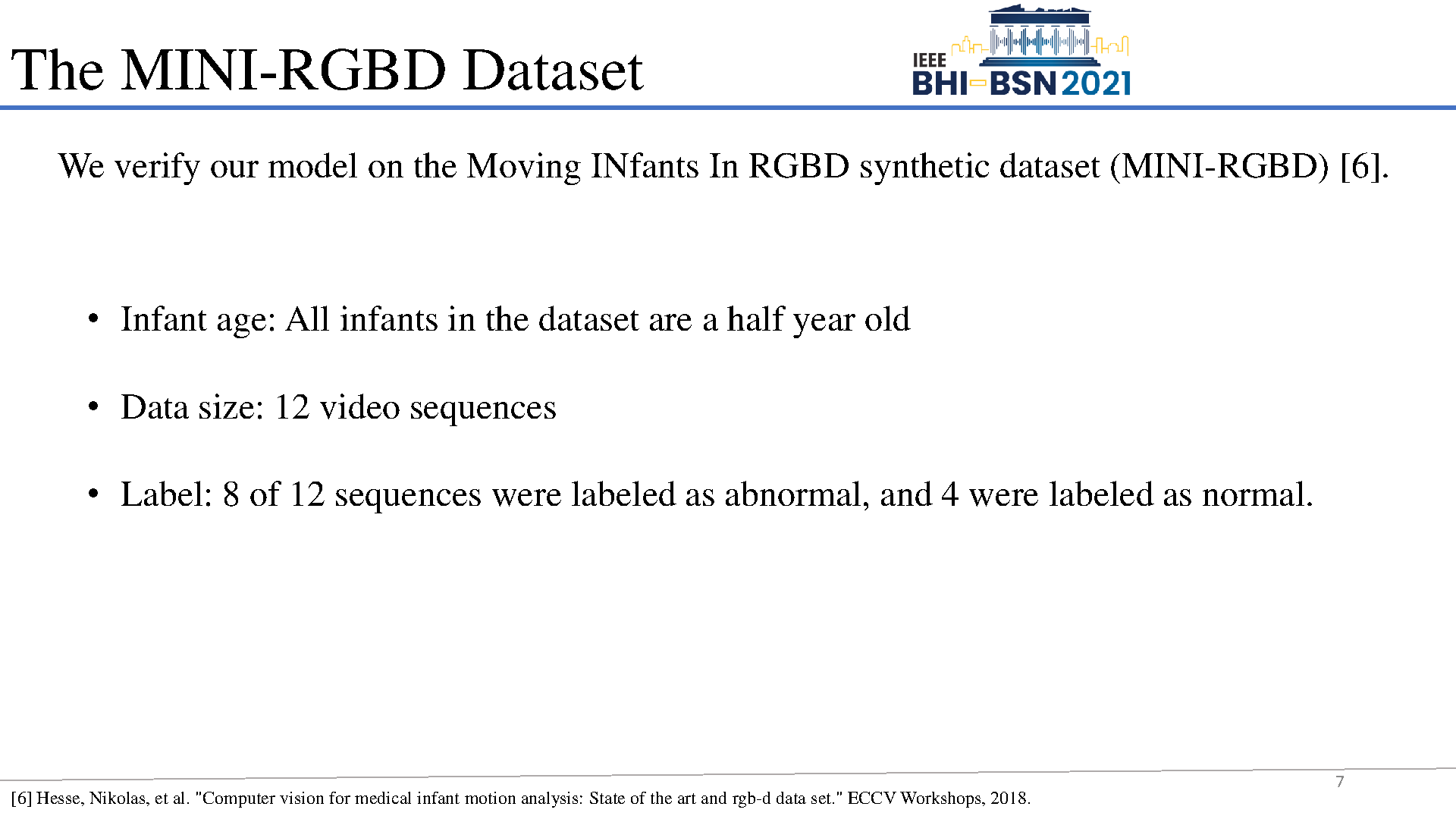
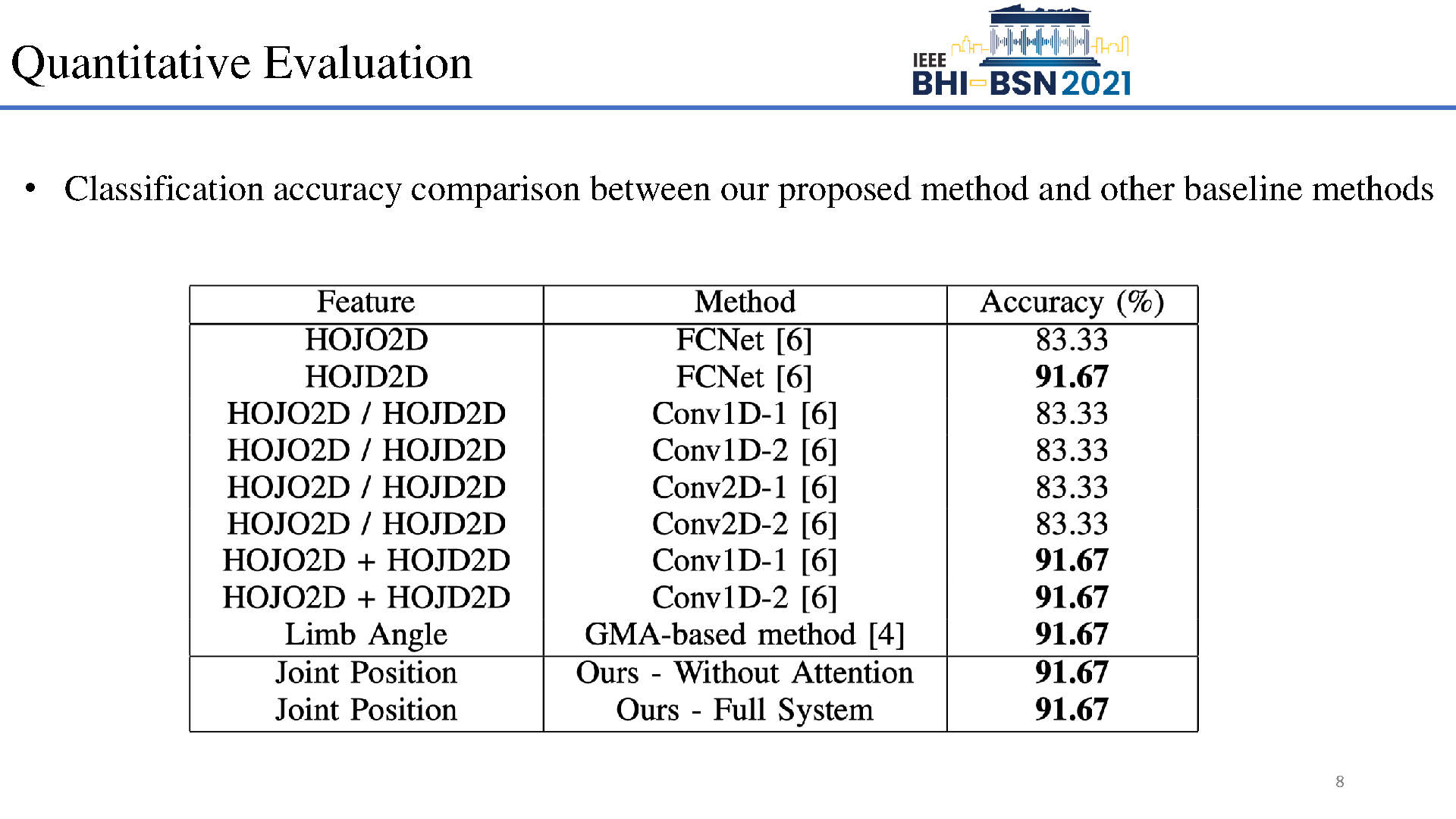
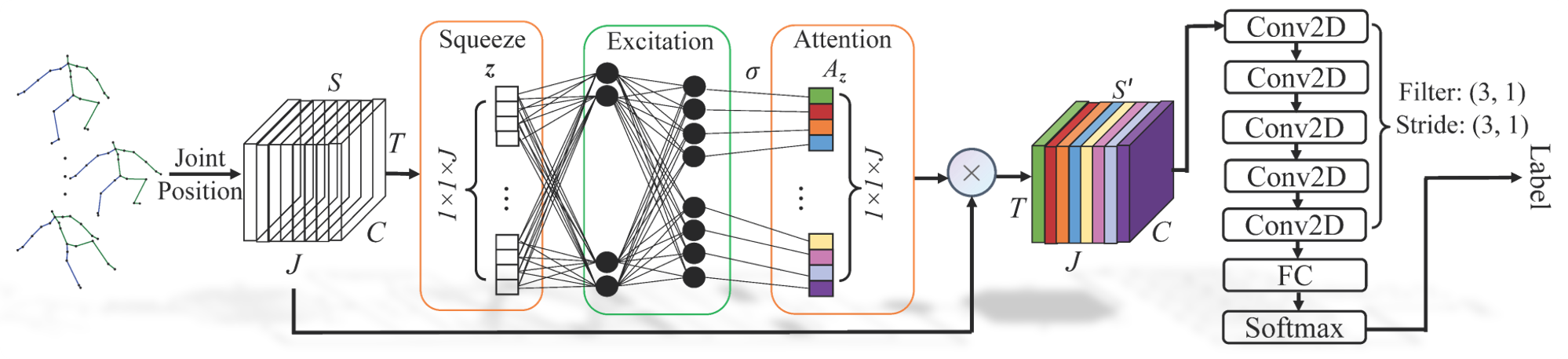
Early prediction of cerebral palsy is essential as it leads to early treatment and monitoring. Deep learning has shown promising results in biomedical engineering thanks to its capacity of modelling complicated data with its non-linear architecture. However, due to their complex structure, deep learning models are generally not interpretable by humans, making it difficult for clinicians to rely on the findings. In this paper, we propose a channel attention module for deep learning models to predict cerebral palsy from infants' body movements, which highlights the key features (i.e. body joints) the model identifies as important, thereby indicating why certain diagnostic results are found. To highlight the capacity of the deep network in modelling input features, we utilize raw joint positions instead of hand-crafted features. We validate our system with a real-world infant movement dataset. Our proposed channel attention module enables the visualization of the vital joints to this disease that the network considers. Our system achieves 91.67% accuracy, suppressing other state-of-the-art deep learning methods.
Publication
Interpreting Deep Learning based Cerebral Palsy Prediction with Channel Attention by Qianhui Men and Hubert P. H. Shum in 2023
Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI)
Links and Downloads
YouTube